Choosing the right heating and cooling system for your home is more important than you might think. It affects your comfort, energy bills, and even the environment. Whether you’re building a new home or upgrading your current system, understanding the options available to you is crucial.
In this article, we will dive into a friendly comparison of two popular options: heat pumps and air conditioners. We’ll break down how each system works, weigh their pros and cons, and help you decide which is best for your needs. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of which system will keep you comfortable year-round while being kind to both your wallet and the planet.
Understanding Heat Pumps
What Are Heat Pumps?
Heat pumps are an essential part of modern HVAC systems, providing both heating and cooling for your home. They work by transferring heat from one place to another. In the summer, a heat pump extracts heat from inside your home and moves it outside, cooling your living space. In the winter, the process reverses: the heat pump pulls heat from the outside air (even when it’s cold) and brings it indoors, keeping your home warm and cozy.


Different Types of Heat Pumps
There are three main types of heat pumps, each with its own unique way of harnessing heat:
- Air-Source Heat Pumps: These are the most common type, especially popular in mild climates like California. They transfer heat between your house and the outside air.
- Ground-Source (Geothermal) Heat Pumps: These systems transfer heat between your home and the ground. They are highly efficient and can provide consistent heating and cooling, but they require significant installation work and cost more upfront.
- Water-Source Heat Pumps: These systems use water sources, such as a lake or well, to exchange heat. They are less common but can be very efficient in the right conditions.
Advantages of Heat Pumps
- Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings: Heat pumps are incredibly efficient because they move heat rather than generate it. This can lead to significant savings on your energy bills compared to traditional heating and cooling systems.
- Heating and Cooling Capabilities: A heat pump is a two-in-one system, providing both heating and cooling. This means you don’t need separate units for winter and summer, saving space and money.
- Environmental Benefits: Since heat pumps use electricity and transfer heat rather than burning fossil fuels, they have a much lower carbon footprint. This makes them a greener choice for environmentally conscious homeowners.
Disadvantages of Heat Pumps
- Higher Upfront Costs: Heat pumps can be more expensive to purchase and install compared to traditional HVAC systems. However, the long-term energy savings often offset these initial costs.
- Performance in Extreme Temperatures: While heat pumps are highly efficient in moderate climates, their performance can drop in extremely cold temperatures. In such cases, an auxiliary heating system may be needed to maintain comfort.
- Maintenance Requirements: Like any HVAC system, heat pumps require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity. This includes biannual check-ups and occasional servicing to keep everything running smoothly.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Energy Efficiency | Higher Upfront Costs |
| Moves heat instead of generating it, leading to lower energy bills. | More expensive to purchase and install compared to traditional HVAC systems. |
| Heating and Cooling | Performance in Extreme Temperatures |
| Provides both heating and cooling, eliminating the need for separate systems. | Efficiency drops in extremely cold temperatures; may need auxiliary heating. |
| Environmental Benefits | Maintenance Requirements |
| Uses electricity, reducing carbon footprint compared to fossil fuels. | Requires regular biannual maintenance for optimal performance. |
Understanding these aspects of heat pumps will help you make an informed decision about whether they are the right choice for your home. Stay tuned as we dive into the specifics of air conditioners in the next section!
Understanding Air Conditioners
What Are Air Conditioners?
Air conditioners are designed to cool your home by removing heat from the indoor air and expelling it outside. They work through a refrigeration cycle that involves a compressor, condenser coils, and evaporator coils. Warm air from inside your home is blown over the evaporator coils filled with refrigerant, which absorbs the heat and cools the air. The cooled air is then circulated back into your home, while the absorbed heat is expelled outside through the condenser coils.
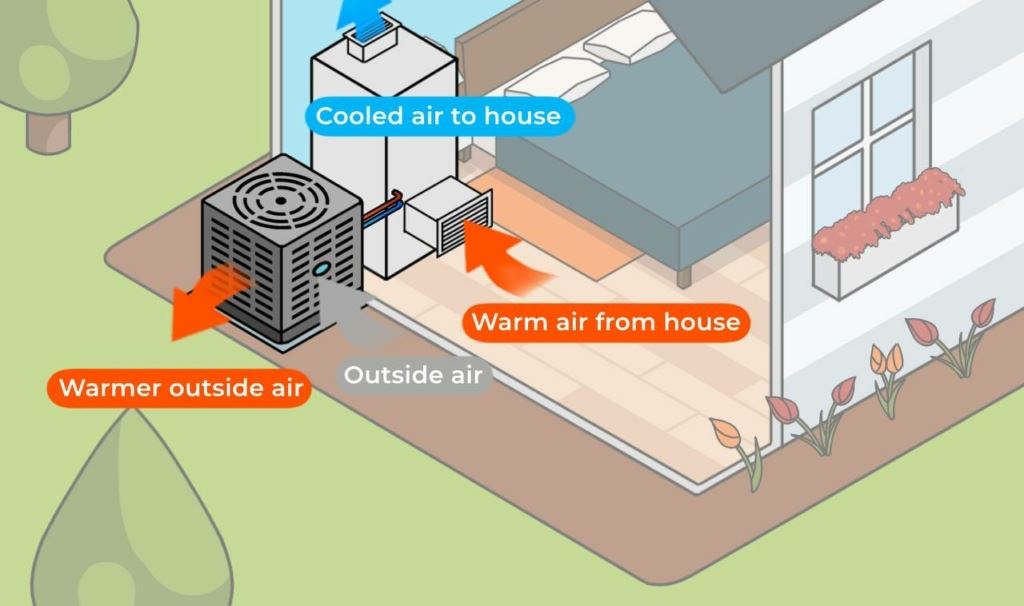
Different Types of Air Conditioners
- Central Air Conditioners: These systems cool your entire home through a network of ducts. They are powerful and efficient for larger spaces.
- Split Air Conditioners: Comprising an indoor and an outdoor unit, these systems are ideal for cooling specific areas or rooms in your home without ductwork.
- Window Air Conditioners: Compact units installed in a window, perfect for cooling individual rooms. They are easy to install and relatively inexpensive.
- Portable Air Conditioners: These units can be moved from room to room and are a flexible solution for cooling specific areas without permanent installation.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Air Conditioners
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Effective Cooling in Hot Climates | Higher Energy Consumption |
| Designed to efficiently cool homes even in the hottest weather. | Tend to use more electricity compared to heat pumps. |
| Lower Initial Costs | Limited to Cooling Only |
| Generally cheaper to purchase and install than heat pumps. | Cannot provide heating, requiring a separate system for winter. |
| Variety of Models | Environmental Impact |
| Multiple options available to suit different needs and spaces. | Uses refrigerants and electricity, contributing to environmental concerns. |
By understanding these key aspects of air conditioners, you can better determine whether they meet your needs for cooling your home. In the next section, we’ll compare heat pumps and air conditioners directly to help you make the best choice.
Comparing Heat Pumps and Air Conditioners
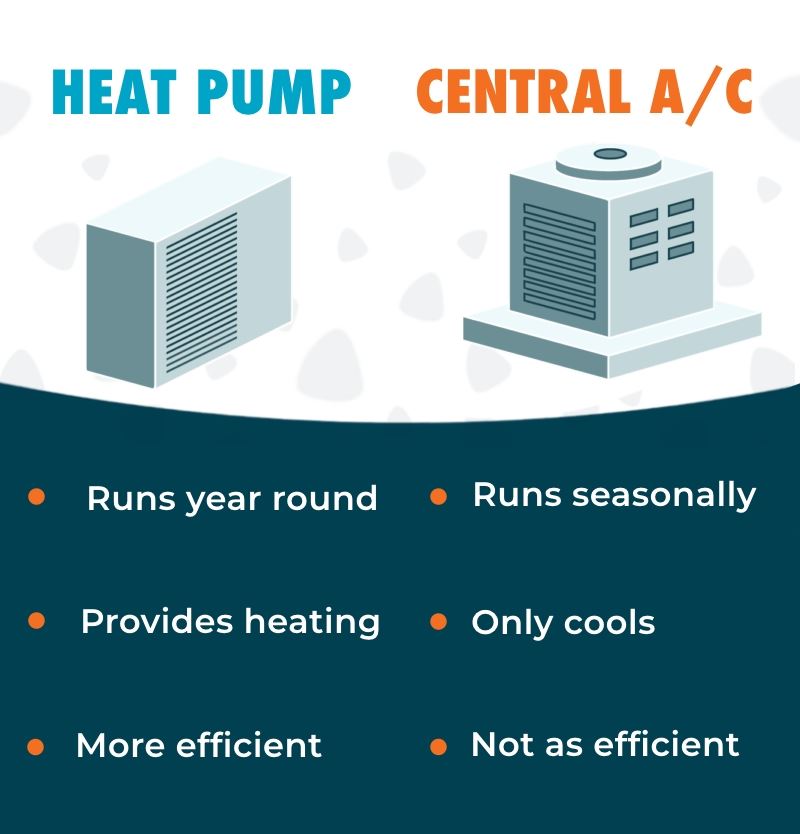
Energy Efficiency
When it comes to energy efficiency, understanding the metrics used to measure it is crucial. The Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) is a key metric that measures the cooling efficiency of both heat pumps and air conditioners. The higher the SEER rating, the more efficient the unit is. Heat pumps often have high SEER ratings, making them very efficient in cooling mode.
For heating efficiency, heat pumps use the Heating Seasonal Performance Factor (HSPF). A higher HSPF means better efficiency during the heating season. Air conditioners don’t have an equivalent metric since they don’t provide heating, so this is a unique advantage of heat pumps.
Functionality
One of the main differences between heat pumps and air conditioners is their functionality. Heat pumps are versatile systems that can both heat and cool your home. This dual capability makes them useful year-round, providing comfort in both summer and winter. In contrast, air conditioners are designed solely for cooling. They are perfect for keeping your home cool during the hot months but require a separate heating system for winter.
Climate Suitability
Climate plays a significant role in determining whether a heat pump or an air conditioner is more suitable for your home. Heat pumps are highly efficient in moderate climates, where they can effectively provide both heating and cooling. They are also effective in hot climates but may not be as efficient as air conditioners in extreme heat. In very cold climates, heat pumps become less efficient and might need an auxiliary heating source to maintain comfort.
Air conditioners, on the other hand, are ideal for cooling in very hot climates. They perform exceptionally well in high temperatures but are not suitable for cold climates since they can’t provide heating.
Installation and Maintenance
The installation process and costs for heat pumps and air conditioners can vary significantly. Heat pumps, due to their dual functionality, have a more complex installation process and typically higher upfront costs. They also require biannual maintenance to ensure both the heating and cooling components are functioning optimally.
Air conditioners generally have a simpler installation process and lower initial costs. They usually require annual maintenance, which is often sufficient to keep them running efficiently. Maintenance costs for air conditioners are typically lower compared to heat pumps, but this can vary based on usage and the specific system type.
Environmental Impact
Considering the environmental impact, heat pumps have a lower carbon footprint compared to air conditioners. They use electricity and are highly efficient, which helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Heat pumps can also utilize renewable energy sources, further enhancing their environmental benefits.
Air conditioners, while effective for cooling, rely on refrigerants and electricity, which can contribute to environmental harm. They are less environmentally friendly compared to heat pumps, particularly due to the use of refrigerants that can affect the ozone layer.
Making the Right Choice for Your Home

Choosing between a heat pump and an air conditioner involves considering several factors to ensure you select the system that best fits your needs. Here are some key aspects to keep in mind:
Factors to Consider
Climate
If you live in a moderate climate like much of California, a heat pump can be an excellent choice due to its ability to both heat and cool efficiently.
In areas with extremely cold winters, an air conditioner paired with a furnace might be more suitable since heat pumps can struggle to maintain efficiency in very low temperatures.
Budget
As it was mentioned above, heat pumps typically have higher upfront costs but can lead to long-term savings on energy bills due to their efficiency.
Air conditioners generally cost less initially, but when combined with a separate heating system, the overall expense can be higher. Consider the total cost of ownership, including installation, operation, and maintenance.
Existing Systems
If you already have a reliable heating system, adding an air conditioner might be the most cost-effective solution.
For homes without existing ductwork, a ductless mini-split heat pump can be an efficient and less invasive option.
Personal Preferences and Usage Patterns
Your personal preferences and how you use your HVAC system also play a crucial role in your decision:
- Year-Round Comfort: If you prefer a system that provides consistent comfort throughout the year, a heat pump’s dual functionality might be ideal.
- Seasonal Use: If you primarily need cooling during the hot months and have a separate heating solution for winter, an air conditioner could suffice.
- Environmental Concerns: For those who prioritize eco-friendly solutions, heat pumps offer significant environmental benefits due to their lower carbon footprint and potential use of renewable energy.
How to Evaluate Your Specific Needs
Assess Your Home’s Characteristics
- Size and Layout: Larger homes might benefit from the comprehensive coverage of a central air conditioning system, while smaller or segmented spaces could be well-served by a ductless heat pump.
- Insulation and Windows: Homes with good insulation and energy-efficient windows can maximize the benefits of either system.
Energy Usage Patterns
Consider your average energy consumption and how a new system might impact your bills. High-efficiency models can offer substantial savings over time.
Professional Consultation
Have a professional HVAC technician evaluate your home. They can provide expert recommendations based on an assessment of your specific needs, existing infrastructure, and local climate.
Making the right choice for your home’s heating and cooling needs involves balancing your climate, budget, and personal preferences. By considering these factors and evaluating your specific requirements, you can select the system that will keep you comfortable and efficient year-round. If you need further guidance, IRBIS HVAC’s team of experts is always ready to help you make an informed decision.
Conclusion
Choosing the right HVAC system for your home is a significant decision that impacts your comfort, energy bills, and the environment. Let’s recap the key points we’ve discussed to help you make an informed choice:
| Aspect | Heat Pumps | Air Conditioners |
| Functionality | Provides both heating and cooling. | Only provides cooling. |
| Energy Efficiency | Highly efficient; potential for long-term savings on energy bills. | Less efficient; higher energy consumption. |
| Climate Suitability | Best for moderate climates; efficiency drops in extreme cold. | Ideal for very hot climates; requires a separate heating system for cold weather. |
| Installation Costs | Higher upfront costs due to complex installation. | Lower initial costs; simpler installation. |
| Maintenance | Requires biannual maintenance; potentially higher maintenance costs. | Requires annual maintenance; generally lower maintenance costs. |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint; environmentally friendly due to use of electricity and potential for renewable energy. | Higher carbon footprint; uses refrigerants that can impact the environment. |
| Overall Cost | Higher initial investment; potential long-term savings through efficiency and possible rebates/incentives. | Lower initial costs; may be more expensive in the long run due to higher energy consumption. |
At IRBIS HVAC, we pride ourselves on our expertise in helping customers choose the right HVAC system for their unique needs. Our team of professionals is dedicated to providing top-notch advice and installation services, ensuring your home remains comfortable and efficient year-round.
We encourage you to reach out to IRBIS HVAC for personalized recommendations and professional installation services. Visit our website or today for a consultation. Let us help you find the perfect HVAC solution for your home!
FAQs
What are the maintenance requirements for heat pumps?
Heat pumps require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Key maintenance tasks include:
- Biannual Professional Check-Ups: Have a technician inspect and service your heat pump twice a year.
- Filter Changes: Replace or clean filters every 1-3 months.
- Outdoor Unit Maintenance: Keep the outdoor unit clear of debris, leaves, and snow.
- Check Refrigerant Levels: Ensure proper refrigerant levels to maintain efficiency.
- Inspect Ductwork: Check for leaks or blockages in the ductwork.
How do I determine the right size heat pump or air conditioner for my home?
To determine the right size HVAC system for your home:
- Professional Assessment: Have an HVAC technician perform a load calculation to evaluate your home’s specific heating and cooling needs.
- Consider Home Size and Layout: Larger homes or homes with complex layouts may require more powerful systems.
- Insulation and Windows: Well-insulated homes with energy-efficient windows can manage with smaller units.
- Local Climate: Take into account the typical weather conditions in your area.
Can heat pumps be used in extremely cold climates?
Heat pumps can be used in extremely cold climates, but their efficiency decreases as temperatures drop. In such cases:
- Auxiliary Heating: Many heat pumps have built-in auxiliary or supplemental heating elements to provide additional warmth.
- Cold Climate Heat Pumps: Some models are designed specifically for colder climates and can operate efficiently at lower temperatures.
- Hybrid Systems: Combining a heat pump with a traditional heating system, like a furnace, can ensure consistent comfort even in very cold weather.
What are the common issues with air conditioners and how can they be fixed?
Common issues with air conditioners include:
- Refrigerant Leaks: Low refrigerant levels can cause inefficient cooling. A professional should repair leaks and recharge the system.
- Dirty Filters: Clogged filters reduce airflow and efficiency. Replace or clean filters regularly.
- Thermostat Problems: Faulty thermostats can lead to incorrect temperature readings and poor performance. Check and recalibrate or replace as needed.
- Drainage Issues: Blocked drain lines can cause water damage and mold growth. Ensure the drain line is clear.
- Electrical Problems: Faulty wiring or connections can prevent the system from working. Have a technician inspect and repair electrical components.
How long do heat pumps and air conditioners typically last?
- Heat Pumps: Generally last 10-15 years. Proper maintenance can extend their lifespan.
- Air Conditioners: Typically last 15-20 years. Regular upkeep can prolong their life, with high-quality systems lasting up to 25 years.
Are there any government incentives or rebates for installing energy-efficient heat pumps or air conditioners? Yes, there are various incentives and rebates available:
- Federal Tax Credits: You may be eligible for tax credits for installing energy-efficient systems.
- State and Local Rebates: Many states and local utilities offer rebates for energy-efficient HVAC installations.
- ENERGY STAR® Incentives: Products that meet ENERGY STAR® criteria often qualify for additional rebates and incentives.
- Check with Local Authorities: Always check with local and state programs for the most current incentives.
How do I improve the energy efficiency of my existing HVAC system?
To improve your HVAC system’s energy efficiency:
- Regular Maintenance: Ensure regular professional inspections and maintenance.
- Seal Ductwork: Check and seal any leaks in your ductwork.
- Upgrade Thermostat: Use a programmable or smart thermostat to optimize heating and cooling schedules.
- Improve Insulation: Properly insulate your home to reduce the load on your HVAC system.
- Clean or Replace Filters: Keep filters clean or replace them regularly to maintain good airflow.
- Consider Zoning Systems: Zoning systems allow you to control temperatures in different areas of your home independently, improving overall efficiency.
The post Heat Pumps Vs Air Conditioners: Which is better? appeared first on IRBIS Heating, Air & Plumbing | www.irbishvac.com.

