
Introduction
Heat pumps are emerging as the unsung heroes of home climate control, captivating homeowners with their remarkable ability to both heat and cool homes efficiently. With innovations in technology, these versatile systems are now suitable for a wider range of climates than ever before. Whether you’re battling scorching summers or freezing winters, a heat pump can keep your home perfectly comfortable year-round.
But choosing the right heat pump system for your home is crucial. An undersized or incorrectly selected system can lead to high utility bills and inefficient operation, while an oversized system may cause uncomfortable temperature fluctuations and unnecessary wear and tear. That’s why understanding the key features and benefits of heat pumps is essential.
Benefits of Heat Pumps
| Energy Efficiency | They transfer heat instead of generating it, using much less energy than conventional heating systems. Contemporary models feature a Coefficient of Performance (COP) of 3.0 or higher, delivering three units of heat for every unit of electricity used. |
| Dual Heating/Cooling Capabilities | With the flick of a switch, a heat pump seamlessly transitions from heating in winter to cooling in summer, simplifying climate control and reducing maintenance and installation costs. |
| Environmental Impact | Heat pumps can dramatically reduce your carbon footprint due to their energy efficiency, especially when using environmentally friendly refrigerants with low global warming potential, and when paired with renewable energy sources like solar panels, they can contribute to net-zero energy goals. |
| Comfort and Flexibility | Enjoy precise temperature control and consistent, reliable indoor comfort with heat pumps, which come in various configurations (ducted, ductless, ground source) to adapt to your home’s unique layout and zoning needs. |
Growing Popularity of Heat Pumps
The growing popularity of heat pumps is no accident. More and more homeowners are discovering their efficiency and flexibility. In Europe, heat pump sales have doubled in the past decade, while the United States has seen a surge in adoption due to federal incentives and rebates aimed at reducing carbon emissions.
Importance of Selecting the Right System
Choosing the right heat pump isn’t just about picking the first one that catches your eye. A heat pump is a significant investment in your home’s comfort and energy efficiency. Selecting the right system ensures you:
- Maximize energy savings and reduce utility bills.
- Enjoy consistent, comfortable indoor temperatures year-round.
- Extend the lifespan of your system with proper sizing and installation.
In this guide, we’ll explore the different types of heat pumps, break down how they work, and offer practical tips to help you choose the best system for your home. Whether you’re aiming to lower your energy bills, shrink your carbon footprint, or simply upgrade your home’s comfort, this guide will help you make a well-informed decision.
How Heat Pumps Work
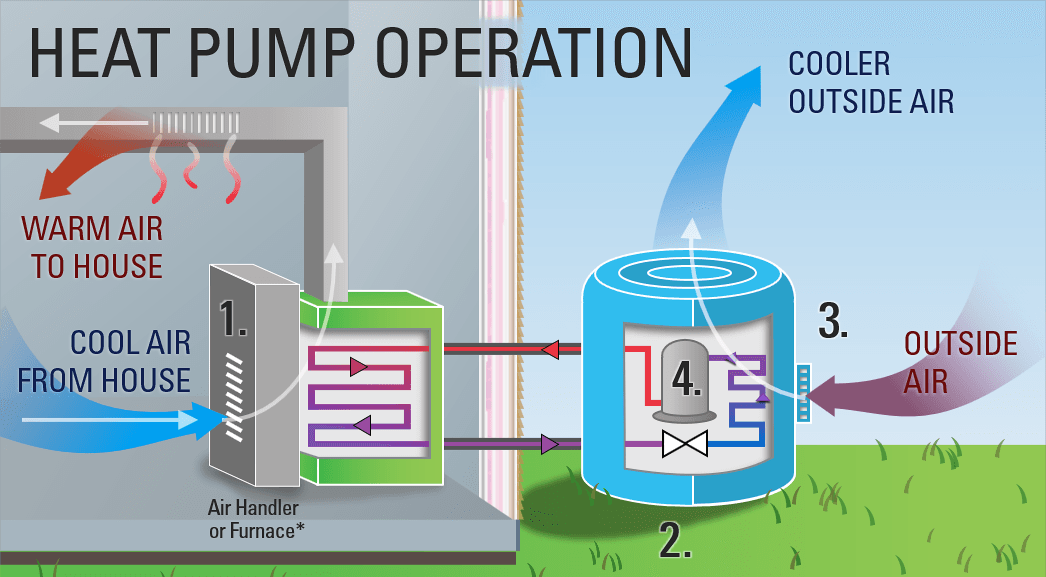
Heat pumps operate on a simple yet clever principle: they transfer heat from one place to another using a refrigeration cycle. This ability to both heat and cool makes them incredibly versatile.
Basic Principles: Heat Transfer and Refrigerant Cycle
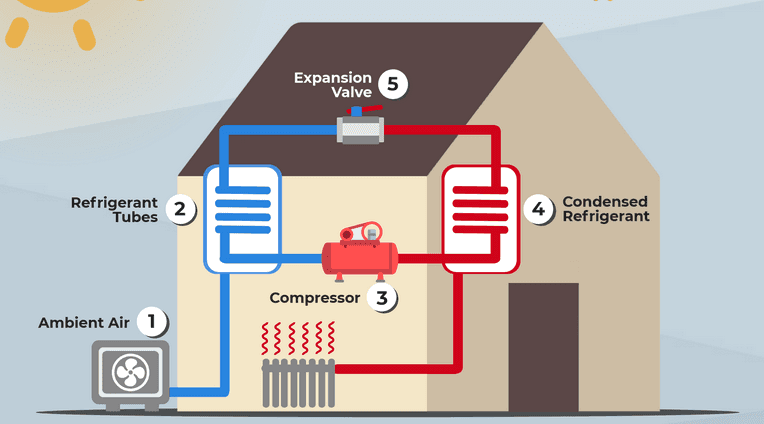
A heat pump comprises four main components:
- Evaporator Coil: Absorbs heat from the surrounding air or ground.
- Compressor: Increases the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant.
- Condenser Coil: Releases heat absorbed by the evaporator coil into the home (for heating) or outside (for cooling).
- Expansion Valve: Reduces the pressure of the refrigerant, cooling it down before it returns to the evaporator coil.
Explanation of Heating and Cooling Modes
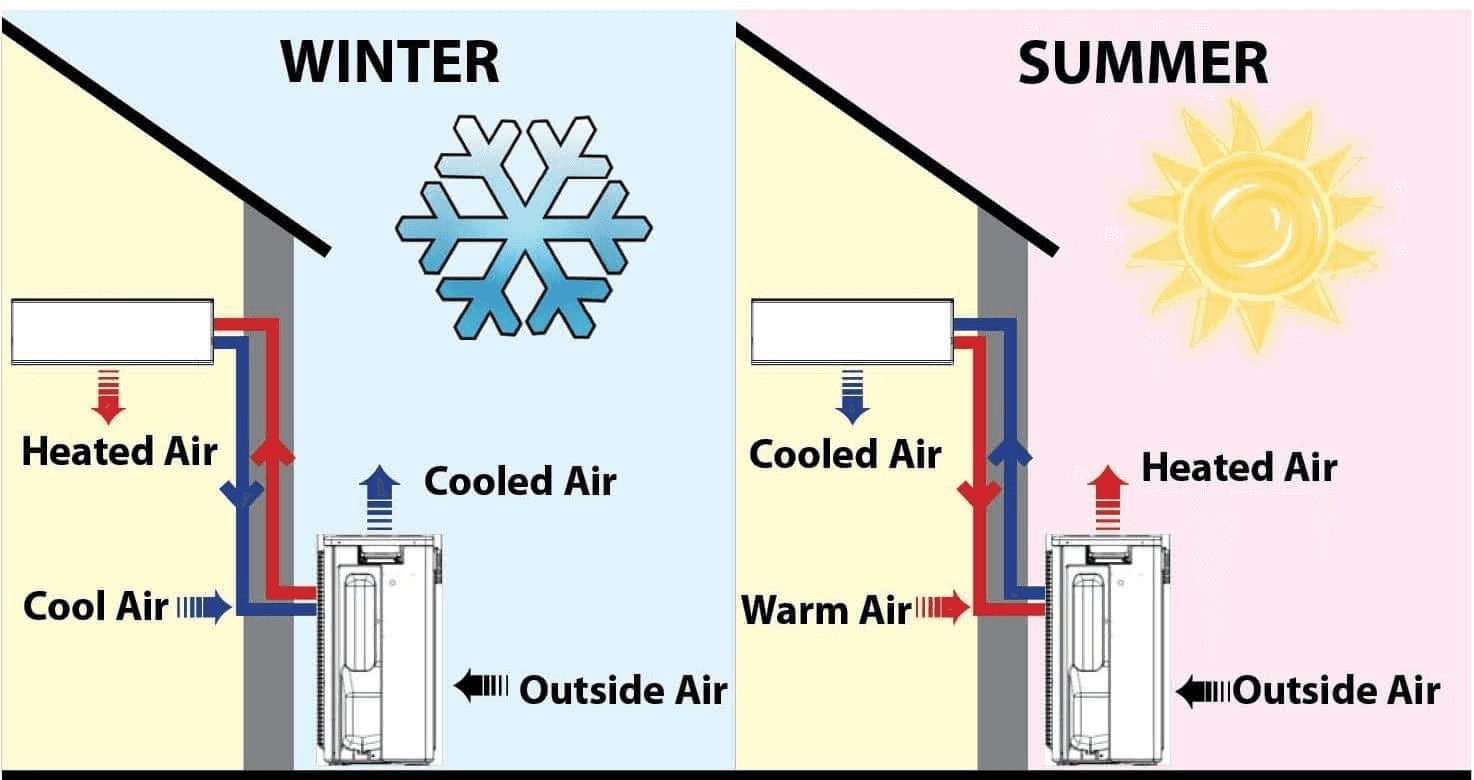
Heating Mode
- The evaporator coil absorbs heat from outside air or the ground.
- The refrigerant, now in gaseous form, flows to the compressor, where it is pressurized and heated further.
- The hot gas passes through the condenser coil inside the home, releasing heat to warm the interior.
- The refrigerant, now cooler and in liquid form, flows through the expansion valve and back to the evaporator to restart the cycle.
Cooling Mode
- The cycle reverses, with the evaporator coil inside the home acting as a cooling element.
- The evaporator absorbs heat from indoor air, and the refrigerant flows to the compressor.
- The compressed refrigerant passes through the condenser coil outside, releasing heat into the outdoor air.
- The cooled refrigerant then returns through the expansion valve to the evaporator inside the home to continue cooling.
Diagram Illustrating the Heat Pump Cycle

- The compressor (center) acts as the “heart” of the system, driving the cycle.
- The direction of heat flow changes between heating and cooling modes using a reversing valve.
- By mastering this heat transfer process, heat pumps can efficiently maintain comfortable temperatures in your home, regardless of the weather outside.
Types of Heat Pumps
Heat pumps come in various configurations, each tailored to different climates, building layouts, and homeowner needs. Here’s a detailed look at the different types:
Air Source Heat Pumps (ASHPs)
Air Source Heat Pumps transfer heat between the outdoor air and your home. They’re the most common type due to their relatively low installation costs and suitability for a wide range of climates.
Split-System vs. Packaged Units
Split-System
- Components: Separate indoor and outdoor units. The outdoor unit contains the condenser and compressor, while the indoor unit contains the evaporator coil.
- Installation: Commonly used for ducted systems where the indoor unit is placed in the basement, attic, or utility closet.
- Benefits: More installation flexibility and higher efficiency due to the separation of components.
Packaged Units
- Components: All-in-one unit that houses the compressor, condenser, and evaporator coil in a single cabinet.
- Installation: Usually placed on the rooftop or next to the building.
- Benefits: Ideal for smaller spaces or buildings without suitable indoor space for split systems.
Ducted vs. Ductless
Ducted Systems
- Use existing ductwork to distribute heated or cooled air throughout the home.
- Suitable for whole-house climate control.
- Limitations: Installation costs can be higher if new ductwork is needed.
Ductless Systems (Mini-Split Heat Pumps)
- Individual indoor units are installed in specific rooms or zones and connected to an outdoor compressor.
- Ideal for zoning, additions, or homes without existing ducts.
- Benefits: High efficiency, installation flexibility, and independent zone control.
Benefits and Limitations
Benefits
- Energy Efficiency: Can achieve up to 300% efficiency in moderate climates.
- Installation: Lower installation cost compared to geothermal systems.
- Versatility: Can handle both heating and cooling.
Limitations
- Climate Dependency: Reduced efficiency in extremely cold climates.
- Outdoor Space Requirement: Requires outdoor space for the compressor unit.
Ground Source Heat Pumps (GSHPs)
Ground Source Heat Pumps, also known as geothermal heat pumps, transfer heat between your home and the ground, where temperatures remain relatively stable year-round.
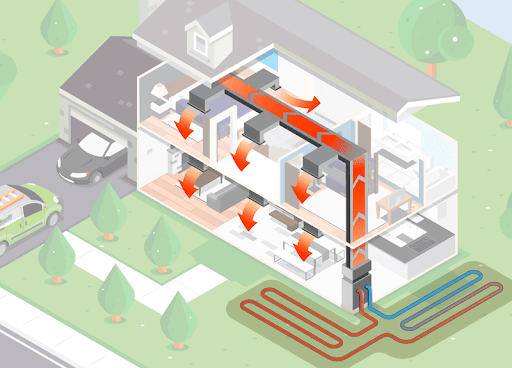
Open-Loop vs. Closed-Loop Systems
Open-Loop Systems:
- Extract water directly from a well or surface water source and discharge it back into the same or a different source.
- Efficiency: Very efficient due to consistent groundwater temperatures.
- Limitations: Requires a suitable water source, and water quality can affect performance.
Closed-Loop Systems:
- Circulate a water-antifreeze mixture through a loop of buried pipes.
Vertical Loops:
- Boreholes drilled 100-400 feet deep.
- Suitable for areas with limited land space.
Horizontal Loops:
- Pipes buried in shallow trenches (4-6 feet deep).
- Requires more land area but is less expensive than vertical loops.
Pros and Cons of Geothermal Systems
Pros:
- High Efficiency: Can reach efficiencies of 400% or higher due to stable underground temperatures.
- Longevity: Ground loops can last up to 50 years.
- Environmental Impact: Reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
Cons:
- High Upfront Cost: Installation can be significantly more expensive due to excavation or drilling.
- Space Requirement: Requires adequate land for horizontal loops or drilling for vertical loops.
Water Source Heat Pumps
Water Source Heat Pumps transfer heat between a water source and the building.
Applications in Multi-Unit Buildings
- Ideal for multi-unit residential buildings, commercial offices, and hotels where a central water loop is maintained.
- Each unit or zone has an individual heat pump, allowing independent climate control.
Efficiency and Versatility
- Efficiency: High efficiency due to stable water temperatures in the central loop.
- Versatility: Can provide both heating and cooling simultaneously to different zones.
Hybrid Heat Pumps
Hybrid Heat Pumps combine a traditional furnace (gas or oil) with an electric heat pump to optimize efficiency.
- Benefits for Extreme Climates
Automatically switches to the most efficient heating method based on outdoor temperatures.
- Cold Weather Efficiency: Heat pump operates efficiently until temperatures drop too low, at which point the furnace takes over.
- Dual-Fuel Savings: Reduces overall heating costs while maintaining comfort.
Mini-Split Heat Pumps
Mini-Split Heat Pumps, or ductless heat pumps, are versatile systems designed for zoning and additions.
Installation Flexibility and Energy Efficiency
Installation:
- Indoor units can be wall-mounted, ceiling-mounted, or floor-mounted.
- Multiple indoor units can be connected to a single outdoor compressor.
Energy Efficiency:
- Zoned climate control reduces energy consumption.
- Inverter technology allows variable-speed operation, minimizing energy waste.
Key Factors in Choosing a Heat Pump
Now that we understand the different types of heat pumps and how they work, it’s important to focus on the key factors that influence which system is right for your home. Let’s dive into what you need to consider to ensure you choose a heat pump that fits your needs, enhances comfort, and saves on energy costs.
Climate and Regional Considerations
Understanding the climate you live in is crucial when selecting a heat pump. The perfect heat pump in Florida might not fare so well in Minnesota due to the vast differences in weather conditions.
- Suitability for Different Climates: Air source heat pumps are typically efficient in mild climates but might struggle in areas with extreme winter temperatures. In contrast, ground source (geothermal) heat pumps excel in almost any climate thanks to their use of stable underground temperatures.
- Cold Climate Heat Pumps (CCHPs) vs. Standard Heat Pumps: Specially designed for frigid environments, CCHPs have advanced features that allow them to operate effectively even when the mercury dips below freezing, making them a hearty choice for northern homeowners.
Home Size and Layout
The architecture of your home dictates your heating needs. A sprawling estate has different demands than a cozy bungalow.
- Proper Sizing: It’s not just about the size of your home but also about its insulation and air seal. A perfectly sized heat pump is efficient and maintains comfortable temperatures effortlessly.
- Zoning Options: Have a multi-story home or areas that are seldom used? Multi-zone systems provide flexibility by allowing you to heat or cool different areas independently, saving energy and money.
Energy Efficiency Ratings
Efficiency ratings aren’t just numbers; they are reflections of performance and potential savings.
- Understanding SEER and HSPF: The Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) and Heating Seasonal Performance Factor (HSPF) ratings gauge cooling and heating efficiencies respectively. Higher ratings mean lower utility bills.
- Look for ENERGY STAR: Products bearing the ENERGY STAR label meet strict energy efficiency guidelines set by the EPA. Choosing an ENERGY STAR certified heat pump ensures you are getting a top-tier energy-efficient product.
Noise Levels
The sound of silence can be golden, especially when it comes to HVAC systems.
- Decibel Ratings: Heat pumps are not all created equal when it comes to noise. Check the decibel ratings to ensure your peace and quiet isn’t disrupted.
- Advanced Noise Reduction: Modern heat pumps are equipped with features like insulated compressor compartments and variable speed fans to minimize operational noise, ensuring your home remains a serene sanctuary.
Installation and Maintenance Costs
A heat pump’s price tag is just the beginning. Consider all associated costs to gauge its true value.
- Balancing Costs: Higher upfront costs might be offset by lower operating costs. Geothermal systems, for example, are expensive to install but typically have very low lifetime costs.
- Maintenance Matters: Regular maintenance can keep your heat pump running efficiently for years. Factor in the ease of maintenance and potential repair costs when choosing your unit.
Incentives and Rebates
Everyone loves a good deal—especially one that makes green technology more accessible.

- Federal Tax Credit: Homeowners can receive a $2,000 tax credit per year for installing eligible heat pump systems.
- Tech Clean: Contractors can claim a rebate of $1,000 through Tech Clean for installing qualifying systems.
- Peninsula Clean Energy: Offers a $2,500 rebate which can be claimed by either the contractor or homeowner.
- Silicon Valley Clean Energy: Provides a substantial $3,100 rebate to homeowners in certain cities.
Choosing the right heat pump is like fitting a piece of a puzzle in your home—it should be just right. Armed with the right information and a clear understanding of your own needs, you can make an informed decision that will bring comfort to your home for years to come.
Comparing Heat Pump Brands and Models
Choosing the right heat pump involves more than just selecting the type; it also means considering which brand and model will best meet your needs. Let’s take a closer look at some of the best heat pump brands and how their models stack up in terms of efficiency, features, and support.
Best Heat Pump Brands
Several manufacturers stand out in the heat pump market due to their reputation for reliability, innovation, and quality. Here are a few leading names:
- Carrier: Known for high-quality, efficient heat pumps, Carrier offers a range of models that are popular for their durability and advanced technology.
- Trane: Trane heat pumps are well-regarded for their energy efficiency and robust performance, even in extreme weather conditions.
- Mitsubishi: Specializing in ductless heat pump systems, Mitsubishi is celebrated for its cutting-edge features and excellent energy savings.
- Daikin: As a leader in air conditioning and heat pump technology, Daikin boasts some of the most efficient systems on the market, with innovative features like inverter technology.
Model Comparisons
When comparing models, consider these key aspects:
- Efficiency Ratings and Performance: Look at the SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) and HSPF (Heating Seasonal Performance Factor) ratings to gauge cooling and heating efficiency, respectively. Models with higher ratings are generally more efficient and can lead to greater energy savings over time.
Features:
- Smart Controls: Many modern heat pumps include Wi-Fi-enabled thermostats that allow you to control your system remotely via a smartphone app, enhancing convenience and potential energy savings.
- Variable-Speed Compressors: These compressors adjust their speed to maintain consistent temperatures more efficiently than single-speed compressors, reducing energy use and wear on the system.
Warranty and Support
A good warranty can protect your investment, while reliable customer support can make maintenance and troubleshooting a smoother experience. Here’s what to look for:
- Warranty Length: Some brands offer longer warranties than others, which can be a testament to the quality of their products. Check the terms to see what components are covered.
- Customer Support: Consider brands that provide accessible, helpful customer service, including ample resources for helping you understand and use your heat pump effectively.
Installation and Sizing Tips
Choosing the right heat pump is a critical decision, but equally important is ensuring it’s properly installed and sized. Incorrect installation or sizing can lead to inefficiency, increased wear and tear, and discomfort. Here are some essential tips to keep in mind:
Importance of Professional Installation
- Expertise: Professional HVAC technicians have the training and experience necessary to install heat pumps correctly, which can prevent future problems and ensure your system operates at peak efficiency. And IRBIS HVAC is ready to be those technicians!
- Safety: Installation involves handling refrigerants and electrical wiring, which can be hazardous without the proper skills and precautions.
- Warranty Requirements: Many manufacturers require professional installation by certified technicians to keep the warranty valid.
Load Calculations and Manual J Analysis
- Purpose: Load calculations determine the precise heating and cooling requirements of your home. A Manual J analysis, which is a detailed load calculation, considers multiple factors including square footage, climate, window types, insulation, and household occupancy.
- Accuracy: Accurate load calculations ensure that the heat pump selected is neither too large (which can cause frequent on/off cycling, wasting energy and stressing the system) nor too small (unable to adequately heat or cool your home).
Correct Sizing to Avoid Short Cycling and Inefficient Operation
- Short Cycling: This occurs when a heat pump is too large for the space it serves, causing it to turn on and off frequently. Not only is this inefficient, but it also puts excessive wear on the system and fails to properly dehumidify the air.
- Efficient Operation: A correctly sized heat pump will run long enough to reach its full efficiency and properly maintain indoor temperature and humidity levels.
Ductwork Considerations for Ducted Systems
- Inspection and Repair: Before installing a new heat pump, existing ductwork should be inspected for leaks, blockages, or insulation issues. Repairing and sealing ducts can greatly improve system efficiency.
- Design: Proper duct design is crucial for efficient airflow. Poorly designed ducts can result in uneven heating or cooling, increased energy costs, and strain on the heat pump.
- Sizing: Like the heat pump itself, ductwork must be properly sized to handle the air volume necessary to achieve efficient temperature and humidity control.
Maintenance and Longevity
Proper maintenance is crucial for maximizing the efficiency, performance, and lifespan of your heat pump. Regular upkeep not only ensures reliable operation throughout the seasons but also prevents minor issues from turning into major problems. Here’s how to maintain your heat pump for optimal longevity.
Regular Maintenance Tasks
- Filter Replacement: One of the simplest yet most effective maintenance tasks. Regularly changing the air filters (typically every 1-3 months depending on usage and type) can prevent airflow restrictions and undue stress on the system.
- Coil Cleaning: The evaporator and condenser coils can accumulate dust and debris, which impairs their ability to absorb and release heat efficiently. Cleaning these coils annually helps maintain your heat pump’s efficiency.
- System Check-ups: It’s important to check the thermostat settings and electrical connections regularly. Tightening electrical connections and ensuring the thermostat is accurately calibrated can significantly affect performance and safety.
Annual Professional Inspection Recommendations
- Comprehensive Assessment: An annual inspection by a qualified HVAC technician should include checking the refrigerant levels, testing the system controls, and ensuring that the heat and cooling cycles are operating properly.
- Ductwork Inspection: If your heat pump is connected to ductwork, the ducts should be inspected for leaks, blockages, or insulation issues, as these can affect system efficiency and your home’s overall comfort.
- Outdoor Unit Inspection: The outdoor unit should be checked to ensure there is no debris obstructing airflow, and the unit should be leveled to guarantee proper drainage.
Expected Lifespan and Signs of Wear
- Lifespan: A well-maintained heat pump typically lasts about 15-20 years. However, factors such as climate, usage patterns, and maintenance frequency can affect this expectancy.
- Signs of Wear:
- Increased Energy Bills: A sudden increase in energy bills can indicate that the heat pump is working harder than usual, possibly due to a maintenance issue.
- Noise: New or increasing noises can be a sign of mechanical wear or an internal component failure.
- Inconsistent Heating or Cooling: If your heat pump is not maintaining the temperature effectively, it may be experiencing issues with the thermostat, refrigerant levels, or compressor.
- Frequent Cycling: Frequent on and off cycling might indicate a malfunction, such as a clogged filter, a wrong thermostat setting, or inadequate refrigerant levels.
Regular maintenance is the key to ensuring your heat pump operates efficiently for many years. By adhering to a maintenance schedule, promptly addressing signs of wear, and scheduling annual inspections, you can enhance your system’s performance and avoid costly repairs. Investing in routine care not only protects your heat pump but also contributes to a more energy-efficient and comfortable home environment.
Making the Final Decision
Choosing the right heat pump for your home is a significant decision that influences not just your immediate comfort but also your long-term energy consumption and savings. As you approach making your final choice, here are the key considerations to keep in mind.
Summarizing the Key Considerations
- Climate Suitability: Select a heat pump that is appropriately designed for the climate where you live. Cold Climate Heat Pumps (CCHPs) for harsh winters, and standard heat pumps for milder conditions.
- Correct Sizing: Ensure the heat pump is correctly sized for your home to avoid inefficiencies, frequent repairs, and energy wastage.
- Energy Efficiency: Consider models with high SEER, HSPF, and COP ratings to ensure maximum efficiency and lower operating costs over the life of the unit.
- Features and Technology: Modern features like smart controls and variable-speed compressors can enhance usability and further improve energy efficiency.
Weighing Upfront Costs Against Long-Term Savings
While the initial cost of a high-quality heat pump can be considerable, it’s essential to evaluate this expense against the potential energy savings over the system’s lifespan. More efficient units often come with higher price tags but can drastically reduce your monthly energy bills. Calculating the payback period—how long it will take for the savings to offset the initial cost—can help you understand the true value of a more efficient system.
Importance of a Reputable Installer
Selecting the right installer is as crucial as choosing the best heat pump. A qualified and reputable installer can ensure that your heat pump is installed according to industry standards, which is vital for optimal performance and durability. IRBIS HVAC, known for its professionalism and high standards, is an excellent choice for installation. With IRBIS HVAC, you can be confident that your heat pump installation will be handled expertly, ensuring that your system operates efficiently from day one.
Conclusion
Investing in a heat pump is a smart choice for homeowners looking to enhance their comfort and efficiency simultaneously. Heat pumps offer a multitude of advantages that make them an ideal solution for heating and cooling needs.
Recap of Heat Pump Advantages
Heat pumps are highly efficient systems that can significantly reduce your home’s energy consumption and carbon footprint. They provide a versatile solution for climate control, capable of both heating and cooling your space with a single unit. With advancements in technology, heat pumps now include features like variable-speed compressors and smart controls, which improve their efficiency and usability. Moreover, their ability to maintain consistent indoor temperatures while being environmentally friendly makes them an increasingly popular choice among homeowners.
Encouragement to Invest in Energy-Efficient Heating and Cooling
The benefits of upgrading to a heat pump extend beyond comfort. Energy-efficient heating and cooling systems like heat pumps not only lower utility bills but also contribute to a more sustainable future by reducing reliance on fossil fuels and decreasing greenhouse gas emissions. Given the long-term savings on energy costs and the potential for government rebates and incentives, the initial higher cost of a heat pump can be a wise investment in your home’s future and the planet.
Final Advice on Choosing the Best System for Your Home
When selecting a heat pump, consider your local climate, the size of your home, and specific household needs to choose a model that is both efficient and effective. Don’t underestimate the importance of having your system professionally installed by reputable technicians like those from Irbis HVAC. Proper installation is crucial to ensuring that the heat pump operates at its peak performance and provides reliable comfort for years to come.
In conclusion, a heat pump offers a robust solution for efficient heating and cooling, making it a worthwhile investment for any homeowner. By choosing the right system and ensuring professional installation, you can enjoy enhanced comfort, lower energy bills, and the peace of mind that comes with a sustainable choice.
FAQ
What is a heat pump and how does it work?
A heat pump is a system that transfers heat from one place to another using refrigeration technology. In the winter, it extracts heat from the outside air or ground and transfers it indoors. In the summer, it reverses the process, removing heat from your home to cool it.
Can heat pumps work in cold climates?
Yes, modern heat pumps are very efficient in cold climates. Cold Climate Heat Pumps (CCHPs) are specifically designed to operate effectively in freezing temperatures, providing reliable heating even when the outside air is very cold.
Are heat pumps expensive to operate?
Heat pumps are generally more energy-efficient than traditional heating and cooling systems like furnaces and air conditioners. While the initial cost can be higher, the operating costs are usually lower due to their efficiency, which translates into long-term savings on energy bills.
How long do heat pumps last?
With proper maintenance, a heat pump can last between 15 to 20 years. Regular servicing and timely repairs are crucial to maximizing the lifespan and efficiency of your heat pump.
Do heat pumps provide both heating and cooling?
Yes, heat pumps are versatile systems that can both heat and cool your home. This dual function makes them an ideal choice for year-round climate control in various weather conditions.
What should I look for when choosing a heat pump?
Key factors to consider include the climate you live in, the size and insulation of your home, and the energy efficiency of the unit. Also, look for features like variable-speed compressors and smart controls, and ensure the system is correctly sized to avoid inefficiency.
How important is the installation of a heat pump?
Professional installation is crucial to the efficient operation of a heat pump. Incorrect installation can lead to inefficiencies, increased wear and tear, and shortened equipment lifespan. It’s recommended to use qualified professionals like those from Irbis HVAC for installation.
What maintenance does a heat pump require?
Regular maintenance tasks include changing the air filter every 1-3 months, cleaning the coils annually, and having a professional check-up at least once a year to ensure optimal performance and to diagnose any potential issues early.
Are there any incentives for installing a heat pump?
Many regions offer tax credits, rebates, or other incentives for installing energy-efficient heat pumps. Check with your local government or energy provider for specific programs available in your area.

